Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom
Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Angular Momentum, Bohr's Atomic Model, Limitations of Bohr Theory, Ground State, Excited State, Transition of Electron, Bohr's Atomic Model for Hydrogen Atom and, Calculation of Wave Number of a Spectral Line
Important Questions on Bohr's Model for the Hydrogen Atom
What are the drawbacks of Bohr's theory?
An electron revolving round in an orbit has angular momentum equal to . Can it lose energy?
On what basis did Bohr assume the concept of stationary orbits for an electron?
Define angular momentum. In the relation , what do and denote?
Calculate the ratio of wavelength of radiation emitted when an electron jumps from third orbit of to the ground state and fifth orbit of to the ground state.
One electron is made to revolve around a proton and it possesses the least possible energy and another electron is made to revolve around an particle with the same energy. Calculate the ratio of the distances of the electrons from the respective species.
An electron is present in a hydrogen atom in the ground state and another electron is present in a single electron species of beryllium. In both the species the distance between the nucleus and electron is same. Calculate the difference in their energies.
Two electronic transitions were found to take place in a single electron species. One is deactivation of electron from the fifth shell to the fourth shell and the other is from the second shell to the first shell. Do the energies emitted due to the above transitions have the same wavelength? Justify.
What is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a hydrogen atom to produce a ion? Explain.
'Electrons jump from one orbit to another orbit.' Justify this statement on the basis of Bohr’s theory.
Bohr's theory can explain the spectra of multielectron species.
Give an equation to calculate the following:
The energy of the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom.
Give an equation to calculate the following:
The radius of the nth orbit of hydrogen atom.
Calculate the ratio of radius of ion in energy level to that of ion in energy level.
Calculate the wavelength of nd spectral line (H) in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum (Given )
Derive the expression for velocity, radius and energy of bohr atom for the Hydrogen atom by using Bohr's postulate.
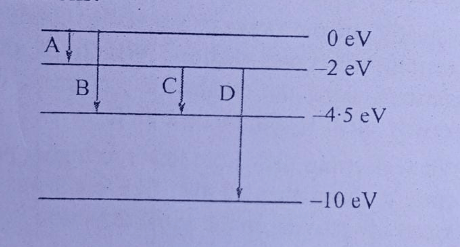
Wavelength of radiation emitted when an electron jumps from a state A to C is and it is when the electron jumps from state B to C. Wavelength of the radiation emitted when an electron jumps from state A to B will be :
The energy levels of an atom of element are shown in the following diagram. which of the level transistions will result in the emission of photons of wavelength ? Support your answer with mathematical caliculations.
What is Bohr's static orbital?
What is Rydberg constant?
